9th November 2023
Can Periodontal Disease Be Cured
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the structures surrounding the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligaments, and alveolar bone. The accumulation of bacteria in the mouth causes it, leading to inflammation and infection. If left untreated, periodontal disease can cause tooth loss and have negative impacts on overall health.
Periodontal disease can be categorised into two main types: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage of the disease and is characterised by red, swollen gums that may bleed easily. If you don’t treat gingivitis promptly, it can progress into periodontitis, which involves the destruction of the supporting tissues and bone around the teeth.
Causes and Risk Factors of Periodontal Disease
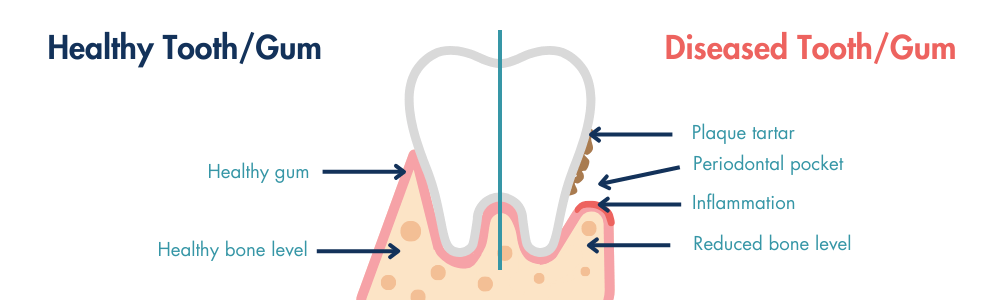
The primary cause of periodontal disease is the build-up of plaque on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film that forms on the teeth and contains bacteria. When plaque is not properly removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional.
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing periodontal disease. These include poor oral hygiene habits, smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause), certain medications, genetic predisposition, and a weakened immune system.
Symptoms and Stages
Recognising the symptoms of periodontal disease is essential for early detection and treatment. In the early stages of gingivitis, symptoms may include red, swollen gums that bleed during brushing or flossing, bad breath, and a receding gumline. As the disease progresses into periodontitis, symptoms become more severe, with the gums pulling away from the teeth, the formation of deep pockets between the gums and teeth, loose teeth, and changes in the bite.
Periodontal disease can be divided into four stages: mild, moderate, severe, and advanced. In the mild stage, there may be slight gum inflammation and bleeding. In the moderate stage, the gums start to recede, and it may affect the bone supporting the teeth. Severe periodontal disease involves significant gum recession and bone loss, while advanced periodontitis can lead to tooth loss.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of periodontitis are crucial for preventing further damage and preserving oral health. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can help identify the disease in its early stages when it is most easily treatable. Dentists can perform a comprehensive examination, including measuring the depth of the gum pockets and taking X-rays to assess bone loss.
If periodontal disease is detected, prompt treatment is necessary to control the infection and prevent its progression. Treatment options will depend on the severity of the disease but may include deep cleaning procedures, such as scaling and root planing, to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line. In more advanced cases, surgical interventions may be required to repair damaged tissues and restore oral health.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
The treatment of periodontitis aims to eliminate infection, reduce inflammation, and restore the health of the gums and supporting structures. The specific treatment plan will depend on the stage and severity of the disease.
For mild cases of periodontal disease, professional dental cleanings and improved oral hygiene practices may be sufficient to control the infection and prevent further damage. This may involve more frequent dental visits for cleanings and the use of antimicrobial mouth rinses.
In moderate to severe cases, professionals typically perform scaling and root planing, also known as deep cleaning. This procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from the surfaces of the teeth and below the gumline. It may require local anaesthesia to ensure patient comfort. In some cases, professionals may prescribe antibiotics or antimicrobial gels to control infection.
Advanced cases of periodontal disease may require surgical interventions. These can include flap surgery, in which experts lift the gums to allow for deep cleaning and repair of damaged tissues, bone grafting to replace lost bone, and tissue regeneration procedures to stimulate the regrowth of gum and bone tissues.
Tips for Preventing Periodontal Disease
Prevention is key when it comes to periodontitis. By following these simple tips, you can reduce your risk of developing the condition:
1. Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss daily, and use an antimicrobial mouthwash to remove plaque and bacteria.
2. Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can help detect and treat periodontal disease in its early stages.
3. Quit smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and makes it harder for the body to fight off infections, including gum disease.
4. Eat a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for gum health.
5. Manage underlying health conditions: Conditions such as diabetes can increase the risk of periodontitis. Work with your healthcare provider to manage any underlying health conditions effectively.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing periodontal disease and maintain a healthy smile.

To learn more about periodontal disease and receive personalised treatment, contact Crescent Lodge Dental Practice in Clapham Common today.
In conclusion, periodontal disease is a common oral health condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. By understanding its causes, recognising the symptoms, and seeking early detection and treatment, you can effectively manage and even cure periodontitis. Remember to follow good oral hygiene practices, visit your dentist regularly, and take proactive steps to prevent the disease. By doing so, you will be well on your way to maintaining a healthy smile and overall well-being.

